In the realm of enigmatic human behaviors, there exists a perplexing phenomenon that intertwines the mysterious realm of dreams with an insatiable appetite that knows no bounds. A deep yearning, a compulsive urge that takes hold and drives individuals to consume, not just for sustenance, but for an elusive fulfillment that can only be found in the depths of their subconscious.
This enigmatic connection between dreams and the ever-present desire to consume the most delectable of morsels is a perplexing riddle that has puzzled experts for generations. It is a craving not driven solely by biological necessity, but one that transcends the boundaries of mere hunger. A puzzle once thought too complex to unravel, yet one that begs for closer examination to understand the intricacies of this occult eating disorder.
Within the intricate web of this appetite-driven aberration lies a tumultuous journey into the labyrinth of human psyche. As the nocturnal realm unfolds its mysterious tapestry, dreams weave themselves into the very fabric of our existence. These nocturnal narratives, often shrouded in symbolism and laden with untapped desires, have the power to unlock hidden recesses of our minds, exposing the deepest and darkest corners of our beings.
Dreams: A Glimpse into the Psyche of Compulsive Eaters

Delving deep into the realm of the subconscious, dreams provide unique insight into the inner world of individuals struggling with compulsive eating habits. These nocturnal visions harbor a wealth of information, offering a window into the intricate web of emotions, fears, and desires that drive the behavior of those affected by this food-related disorder.
When sleep envelops the mind, dreams unfold with vivid intensity, transporting individuals through a journey where the boundaries of reality blur. Within these realms of imagination lie clues that may unlock the psychological underpinnings behind compulsive eating, providing invaluable understanding and potential paths towards recovery.
Symbolism: Dreams possess a language all their own, often steeped in symbolism and metaphor. The images and scenarios that manifest during sleep can reflect deep-seated emotions, fantasies, and unresolved conflicts relating to food and eating. By analyzing these dreams, patterns may emerge, shedding light on the underlying psychological factors that contribute to compulsive eating behaviors.
The Unconscious Mind: Dreams serve as a gateway to the unconscious mind, offering a glimpse into thoughts and emotions that may not be readily accessible during waking hours. Compulsive eaters often grapple with complex emotions tied to food, such as guilt, shame, and a lack of control. Exploring the themes and contents of dreams can provide valuable insights into the psychological factors that contribute to these struggles, allowing for a deeper understanding of the underlying issues at play.
Desires and Triggers: Dreams can unveil the desires and triggers that fuel compulsive eating. Whether it's a recurring dream involving a favorite indulgence or a nightmare centered around loss of control, these nocturnal visions may reveal the subconscious cravings and emotional triggers that drive the unhealthy relationship with food. By deciphering these dreams, individuals can identify and address these underlying desires and triggers to regain control over their eating habits.
In conclusion, dreams act as a mirror reflecting the complex psychological landscape of those affected by compulsive eating. By exploring the symbolism, delving into the unconscious mind, and deciphering desires and triggers, individuals can gain profound insights into the underlying factors of the disorder. Integrating these insights into a comprehensive approach to treatment can help pave the way for a healthier relationship with food and a brighter future.
Unveiling the Underlying Causes of Compulsive Eating through Dream Analysis
Exploring the profound connection between dreams and the development of compulsive eating behaviors can aid in gaining a deeper understanding of the root causes behind this food-related disorder. By delving into the realm of dreams, individuals can unearth valuable insights that shed light on the motivations and triggers driving their compulsive eating habits.
- Insight into subconscious desires: Examining dreams can provide a glimpse into the subconscious desires and cravings that may unknowingly fuel compulsive eating behaviors. Dreams act as a window into the realm of unfulfilled needs or longings, which often manifest themselves through excessive consumption of food.
- Identification of emotional associations: Dreams possess the ability to uncover hidden emotions and unresolved psychological conflicts that contribute to compulsive eating. By decoding the symbolism and themes within dreams, individuals can recognize the emotional associations connected to their eating patterns.
- Revealing underlying traumas: Dreams can unveil hidden traumas that have a profound impact on one's relationship with food. These traumas may stem from past experiences, triggering compulsive overeating as a coping mechanism. By analyzing dreams, individuals can begin the healing process and address these deep-rooted traumas.
- Recognizing patterns and triggers: Through dream analysis, individuals can identify recurring patterns or triggers in their dreams that correlate with compulsive eating episodes. These patterns can shine a light on specific situations, circumstances, or emotions that stimulate the impulse to engage in excessive food consumption.
- Empowering personal growth and healing: Embracing dream analysis as a tool for understanding compulsive eating behaviors empowers individuals to embark on a journey of self-discovery and healing. By unraveling the underlying causes of their food-related disorder, individuals can cultivate greater self-awareness and work towards overcoming their compulsive eating habits.
By recognizing the value of dream analysis in comprehending the complexities behind compulsive eating, individuals can take significant strides towards addressing and ultimately conquering this debilitating disorder.
The Inner Workings of Compulsive Eating: Exploring the Link between Food and Emotions

In this section, we will delve into the intricate relationship that exists between our consumption of food and our emotional state. Here, we aim to uncover the underlying mechanisms behind compulsive eating behaviors, bringing to light the powerful connection between what we eat and how we feel.
Compulsive eating, often characterized by a persistent and overwhelming urge to consume large quantities of food, is not simply a matter of mindless indulgence. Rather, it is a complex interplay between our emotions and our dietary habits. Our relationship with food is often intertwined with our emotional well-being, as it acts as both a source of comfort and a means of escape.
Food, for those struggling with compulsive eating, can serve as a coping mechanism to alleviate emotional distress. It may provide a temporary sense of relief, offering solace in times of stress, sadness, or anxiety. However, this reliance on food as a means of emotional regulation can create a vicious cycle, perpetuating the disordered eating patterns.
Additionally, the type of food we choose to consume can significantly impact our emotional state. Certain foods, such as those high in sugar or fats, have been found to trigger the release of feel-good chemicals in the brain, temporarily uplifting our mood. This biochemical reaction can further reinforce the association between specific foods and positive emotions, fueling the compulsive eating cycle.
Furthermore, the role of emotions in compulsive eating extends beyond the immediate effects of food consumption. Emotional factors, such as stress, depression, or low self-esteem, can also contribute to the development and maintenance of disordered eating behaviors. Emotional triggers and underlying psychological issues often underpin the complex nature of compulsive eating, requiring a comprehensive understanding for effective management and treatment.
In conclusion, exploring the mechanics of compulsive eating entails unraveling the intricate connection between food and emotions. By delving into the interplay between our dietary choices and our emotional state, we can gain insights into the underlying complexities of this disorder, ultimately allowing for more informed approaches to prevention and intervention.
Exploring the Emotional Drivers of Overeating Cycles and Strategies for Breaking Free
Within the complex landscape of food-related challenges, emotions play a significant role in the cycles of overeating. Understanding the powerful influence of emotions on our eating habits is essential in order to break free from the patterns that keep us trapped in unhealthy relationships with food.
Emotional eating is a phenomenon in which individuals turn to food as a way to cope with, or numb, their emotions. The connection between emotions and overeating is often rooted in a desire for comfort, relief, or distraction from difficult feelings. It can become a vicious cycle, as the temporary relief provided by overeating is often followed by feelings of guilt, shame, and further emotional distress.
Identifying and acknowledging the emotions that drive overeating is a crucial step towards breaking free from this cycle. Reflecting on how specific emotions, such as stress, sadness, boredom, or frustration, trigger the desire to overeat can help individuals develop alternative coping mechanisms that do not involve food.
- Stress: Understanding the impact of stress on overeating is essential in finding healthier ways to manage it. Exploring stress reduction techniques such as meditation, exercise, or seeking support from others can help break the association between stress and overeating.
- Sadness: Recognizing the connection between sadness and overeating allows for the development of alternative ways to address and process emotions. Engaging in activities that bring joy, seeking comfort from loved ones, or journaling can provide healthier avenues for dealing with sadness.
- Boredom: When boredom triggers overeating, finding new hobbies or engaging in activities that provide mental stimulation and fulfillment can be beneficial. Exploring creativity, learning new skills, or getting involved in community activities can help redirect the focus away from food.
- Frustration: Finding constructive ways to manage frustration without turning to food is vital. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, engaging in physical activity, or practicing mindfulness can help individuals navigate frustration in a healthier manner.
Breaking free from emotional overeating requires a conscious effort to develop and implement strategies that address the underlying emotions driving these cycles. By recognizing emotional triggers and proactively seeking alternative ways to cope with difficult feelings, individuals can regain control over their relationship with food and establish healthier eating habits.
The Impact of Early Life Trauma on the Development of Compulsive Overeating
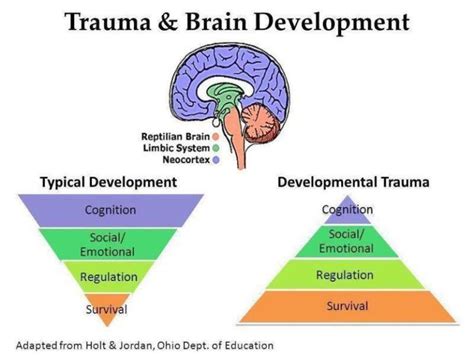
In this section, we will explore the significant influence of childhood trauma on the establishment of compulsive overeating tendencies. Childhood experiences play a crucial role in shaping an individual's relationship with food, and certain traumas can contribute to the development of compulsive overeating as a coping mechanism.
Understanding the lasting effects: Childhood trauma can leave deep emotional scars that persist into adulthood. These traumas, which may include neglect, abuse, or loss, can profoundly impact an individual's self-esteem, emotional well-being, and ability to cope with stress. The repercussions of such experiences often manifest themselves in unhealthy relationships with food.
The link between trauma and compulsive eating: Many individuals who have experienced childhood trauma turn to food for comfort and escape. Compulsive overeating becomes a coping mechanism, providing temporary relief from emotional pain or stress. The act of consuming food becomes a form of self-soothing, serving as a means of distraction and numbing negative emotions.
Vicious cycle of trauma and overeating: The cycle of childhood trauma and compulsive overeating can be self-perpetuating. The overconsumption of food offers temporary relief, but feelings of guilt, shame, and loss of control often follow, reinforcing the negative emotions associated with trauma. This cyclical behavior prevents individuals from addressing their underlying emotional pain and perpetuates the reliance on food for emotional regulation.
Addressing childhood trauma in treatment: Recognizing the role of early life trauma in the development of compulsive eating is crucial for effective treatment. Therapeutic interventions that target both the emotional wounds from trauma and the underlying causes of compulsive overeating can help individuals break free from the cycle and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
In conclusion, childhood trauma has a profound impact on the development of compulsive overeating. By understanding this link and addressing the emotional wounds from trauma, individuals can find healing and establish a healthier relationship with food.
Investigating the Connection between Childhood Trauma and the Development of Food-Related Disorders
In this section, we will delve into the intricate relationship between childhood trauma and the emergence of disorders related to food consumption. By exploring the profound impacts of early life experiences on individuals' relationship with food, we aim to shed light on the underlying factors that contribute to the development of these disorders.
Understanding the Influence of Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma encompasses a range of adverse experiences, including physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. Research suggests that such traumatic events can significantly impact various aspects of individuals' lives, including their relationship with food. It is crucial to investigate the ways in which childhood trauma affects individuals' attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors regarding food, leading to the manifestation of food-related disorders.
Exploring the Emotional Coping Mechanisms
Childhood trauma often creates lasting emotional scars that individuals may struggle to address or manage effectively. As a result, many individuals turn to food as a means of comfort, escaping their emotional pain or seeking temporary relief from distressing feelings. This section aims to examine the complex interplay between emotional coping mechanisms, such as comfort eating, and the traumatic experiences encountered during childhood.
Examining the Role of Attachments and Relationships
The quality of attachments and relationships experienced during childhood plays a vital role in shaping an individual's overall well-being. Disruptions in secure attachments and unstable relationships during formative years can contribute to the development of food-related disorders. By investigating this link, we can gain insights into how early experiences of attachment impact individuals' self-perception and their relationship with food.
Considering the Psychological Associations
Psychological factors related to childhood trauma, such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem, can further exacerbate individuals' vulnerability to developing food-related disorders. This section aims to explore the intricate web of psychological associations, shedding light on the mechanisms through which childhood trauma impacts individuals' thoughts, emotions, and behaviors concerning food.
Identifying the Implications for Treatment and Prevention
Understanding the connection between childhood trauma and the manifestation of food-related disorders is crucial for effective treatment and prevention strategies. By identifying the underlying factors and exploring possible interventions, this section will provide valuable insights into how healthcare professionals can support individuals in their journey towards recovery and minimize the impact of childhood trauma on the development of food-related disorders.
FAQ
Is compulsive eating a common disorder?
Yes, compulsive eating is a common disorder that affects a significant number of individuals worldwide. It is estimated that around 2-5% of the general population struggles with this condition.
What are the potential causes of compulsive eating?
The causes of compulsive eating can vary from person to person. Some potential factors include emotional triggers, past trauma or abuse, genetic predisposition, and certain psychological disorders such as depression or anxiety.
How does compulsive eating affect a person's overall health?
Compulsive eating can have significant negative effects on a person's overall health. It often leads to weight gain and obesity, which can increase the risk of various health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. It can also affect mental and emotional well-being, leading to feelings of guilt, shame, and low self-esteem.
Are there any effective treatments for compulsive eating?
Yes, there are several treatment options available for compulsive eating. These may include therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or dialectical behavior therapy, to address underlying emotional issues and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Support groups, nutritional counseling, and medication may also be utilized as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Can compulsive eating be overcome?
Yes, with proper treatment and support, compulsive eating can be overcome. It may require time and effort, but many individuals have successfully overcome this disorder and gone on to lead healthier, more balanced lives.



