Imagine a kaleidoscope of emotions and scenarios that play out in the intricate realm of sibling dynamics. The intricate dance between brothers and sisters is a subject that has captivated humanity for centuries. From fiery arguments to tender moments of bonding, the sibling relationship is a treasure trove of conflicting sentiments and deep-rooted connections.
Within the tapestry of family life, sibling conflict stands as a mysterious juncture where love and rivalry intertwine. It is a playground where fierce competition and ceaseless comparison often take center stage. In this labyrinth of emotions, one cannot help but question the significance behind these feuds and the hidden messages they convey.
Rooted in biology and psychology, the clashes between siblings can be symbolic of a much larger narrative. Behind the facade of bickering lies a rich landscape of power struggles, identity formation, and the intricate balance of individuality within the familial unit. Understanding the multifaceted nature of sibling discord can offer valuable insights into our own emotions, behaviors, and relationships.
The Psychology Behind Sibling Conflict: Understanding the Dynamics

Sibling conflict is a complex and intriguing aspect of human relationships that often arises within families. This article delves into the psychological factors underlying these conflicts, exploring the dynamics that contribute to the intensity and longevity of such disputes.
At the core of sibling conflicts lies a multifaceted interplay of emotions, needs, and personality characteristics. One significant element is the competition for attention and resources, leading to feelings of jealousy, resentment, and rivalry. Additionally, differences in temperament, interests, and values can exacerbate conflicts, as individuals struggle to coexist and assert their autonomy within the family dynamics.
Furthermore, birth order and parental favoritism play pivotal roles in shaping sibling relationships. The dynamics between older and younger siblings are often influenced by power imbalances and contrasting expectations, which can create friction and a sense of inequality. Likewise, experiences of perceived differential treatment by parents can trigger resentment and discord among siblings.
- Communication breakdown is another critical factor in the escalation of sibling conflicts. Poor communication skills, misunderstandings, and a lack of empathy can fuel confrontations and impede reconciliation attempts. Additionally, unresolved conflicts from early childhood may resurface in adult sibling relationships, indicating the lasting impact of unresolved issues.
- Recognizing the underlying psychological mechanisms that drive sibling conflict can provide valuable insights into effective resolution strategies. Encouraging open and respectful communication, teaching conflict resolution skills, and fostering empathy and understanding can help siblings navigate their differences and establish healthier relationships.
- Moreover, parental mediation and support have a significant impact on the resolution of sibling conflicts. Parents who promote fairness, validate emotions, and establish clear boundaries can mitigate hostility and facilitate cooperation between siblings. Building a sense of teamwork and cooperation within the family can lead to more harmonious sibling relationships.
- Lastly, it is crucial to acknowledge that sibling conflicts can also have positive aspects. They can serve as opportunities for personal growth, skill development, and the formation of problem-solving abilities. Resolving conflicts constructively can foster resilience, empathy, and conflict management skills, which are essential for navigating interpersonal relationships beyond the family context.
In conclusion, understanding the psychological dynamics behind sibling conflict can provide valuable insights into the intricacies of these relationships. By recognizing the underlying factors and implementing effective resolution strategies, individuals and families can strive towards cultivating more harmonious and fulfilling sibling bonds.
An exploration of the underlying psychological factors contributing to rivalry among siblings
In this section, we delve into the intricate dynamics that give rise to conflict between brothers and sisters. By analyzing the underlying psychological factors, we aim to shed light on the origins and complexities of sibling rivalry.
1. Sibling Hierarchies:
One key factor contributing to conflict among siblings is the establishment of hierarchies within the family. As brothers and sisters navigate their place in the family structure, a power struggle often ensues, leading to tension and disagreements.
2. Role of Parental Influence:
The role of parents in shaping sibling relationships cannot be understated. Parental favoritism, differential treatment, or inconsistent discipline can contribute to feelings of resentment and jealousy, fueling the conflict between siblings.
3. Individual Differences:
Each sibling has their own unique personality, temperament, and needs. These individual differences can create friction within the sibling relationship, particularly when siblings have conflicting goals, desires, or expectations.
4. Competition for Resources:
Siblings often find themselves competing for limited resources such as attention, affection, recognition, or tangible items. This competition can lead to intense conflicts as siblings vie for parental approval or strive to establish their own identity within the family dynamic.
5. Emotional Bonds and Attachments:
While conflict may be prevalent among siblings, it is important to recognize the emotional bonds and attachments they share. Sibling relationships can be characterized by a complex mix of love, affection, and rivalry, as siblings navigate their need for individuality while maintaining a sense of connection.
In conclusion, understanding the psychological factors underlying sibling conflict provides valuable insights into the complexities of these relationships. By recognizing and addressing these factors, parents and siblings can work towards healthier and more harmonious relationships, fostering personal growth and emotional well-being.
Common Causes of Sibling Conflict: Uncovering the Triggers
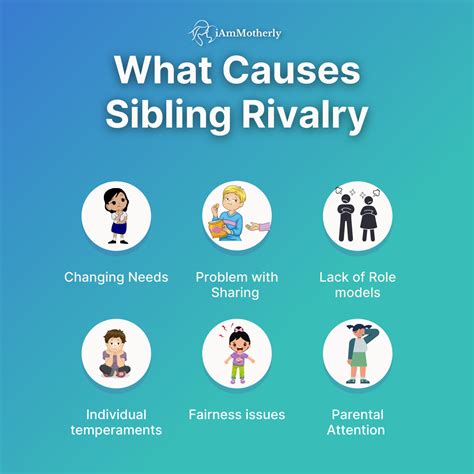
Understanding the root causes of conflicts between brothers and sisters is essential in gaining insight into the dynamics of sibling relationships. By exploring the underlying triggers, we can comprehend the factors that contribute to disagreements and tensions without direct reference to dreams or specific individuals. This article aims to shed light on the common causes that often ignite conflict among siblings, providing a deeper understanding of the complex nature of these relationships.
1. Rivalry: Sibling rivalry, a prevalent phenomenon in family dynamics, occurs when brothers and sisters vie for attention, resources, or parental approval. This intense competition can lead to conflicts over shared possessions, academic achievements, or even perceived favoritism from parents or other family members.
2. Differences in Personality: Siblings, like any individuals, have distinct personalities that can clash. Variances in temperament, interests, and values may create friction as siblings navigate their shared living spaces, make decisions together, or engage in activities that require compromise. These disparities can result in conflicts stemming from misunderstandings and the struggle to find common ground.
3. Power Struggles: As siblings develop and assert their independence, power struggles can emerge. Each sibling may attempt to assert control or dominance within the relationship, leading to conflicts over decision-making, responsibilities, and boundaries. Power imbalances can be a significant trigger, causing tensions and conflicts to escalate.
4. Jealousy: Feelings of jealousy and envy are not uncommon among siblings. When one sibling perceives the other as receiving more attention, success, or privileges, it can lead to resentment and conflicts. Sibling jealousy may stem from perceived inequalities in treatment or experiences, adding fuel to the already complex dynamics between brothers and sisters.
5. Lack of Communication: Communication is a key component of any healthy relationship, and the sibling bond is no exception. When effective communication skills are lacking, misunderstandings can occur, leading to conflicts. Poor communication can manifest as misinterpretation of words, inability to express emotions, or failure to address and resolve underlying issues.
6. Role Confusion: Siblings often have defined roles within the family unit, which can range from being the responsible older sibling to the carefree younger one. When these roles become blurred or individuals resist conforming to them, conflicts can arise. Role confusion may occur due to changing family dynamics, shifting expectations, or individual struggles with identity and self-expression.
7. Limited Resources: Competition for limited resources, such as time, attention, or financial support, can lead to conflicts between siblings. When resources are scarce or unevenly distributed, siblings may vie for a larger share, leading to tensions and disputes.
By delving into these common causes of conflict between siblings, we can gain a greater appreciation for the complexity and challenges inherent in maintaining harmonious relationships within our own families. Recognizing these triggers can help foster understanding and provide insights into strategies for managing and minimizing conflicts in the future.
Analysis of the Dominant Factors Contributing to Conflict Between Siblings
In this section, we will delve into a comprehensive examination of the key factors that commonly give rise to discord amongst brothers or sisters. By exploring the root causes of these conflicts, we aim to gain a deeper understanding of the dynamics that often lead to strained relationships between siblings.
1. Rivalry and Competition: Sibling conflicts frequently stem from the natural inclination of brothers and sisters to compete with one another. Whether it be vying for limited resources, attention from parents, or personal achievements, this sense of rivalry often fuels disagreements and tension within sibling relationships.
2. Differences in Personalities and Temperaments: Variations in individual personalities and temperaments can generate significant clashes between siblings. Divergent traits such as introversion versus extroversion, impulsiveness versus thoughtfulness, or assertiveness versus passivity can easily ignite conflict and misunderstandings within the sibling dynamic.
3. Power Struggles and Hierarchies: Sibling relationships commonly involve power struggles, where each sibling seeks to establish their dominance or authority within the family unit. These power dynamics often create intense conflicts, as brothers and sisters strive to assert themselves and secure their position in the sibling hierarchy.
4. Jealousy and Sibling Favoritism: Feelings of jealousy can arise when siblings perceive preferential treatment from parents or relatives towards one another. Observing unequal distribution of attention, affection, or privileges can provoke strong negative emotions and contribute to ongoing conflict between brothers and sisters.
5. Communication Issues: Ineffective communication, including misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and a lack of active listening, can significantly fuel conflicts between siblings. Difficulties in expressing emotions, needs, and expectations can create tension and resentment, leading to prolonged disagreements and disputes.
6. Past Resentments and Unresolved Issues: Lingering resentments and unresolved issues from the past can resurface in sibling relationships, triggering conflict. Unaddressed grievances, perceived injustices, and unhealed wounds can serve as catalysts for ongoing disagreements and strained interactions between brothers and sisters.
Through a meticulous exploration of these predominant causes of sibling conflict, we can unearth valuable insights into the intricacies of these relationships. By deciphering the underlying reasons behind the conflicts, we may be better equipped to navigate and mitigate the discord, fostering healthier and more harmonious relationships between brothers and sisters.
The Impact of Sibling Conflict on Development: Exploring Long-Term Effects

Understanding the lasting consequences of conflicts between brothers and sisters is a crucial aspect of studying human development. This section aims to delve into the long-term effects of sibling conflict and its implications for individuals' growth and well-being. By examining various dimensions such as emotional, social, and psychological development, we can gain valuable insights into how sibling conflict influences individuals throughout their lives.
| 1. Emotional Development: | Examining the impact of sibling conflict on emotional development allows us to understand how these conflicts shape an individual's ability to regulate emotions, form healthy relationships, and manage stress. Research suggests that repeated and intense sibling conflicts can contribute to heightened levels of anger, anxiety, and depression, impacting emotional well-being into adulthood. |
| 2. Social Development: | Sibling conflict can significantly influence an individual's social development, particularly in terms of interpersonal skills and the formation of peer relationships. Conflicts with siblings provide unique opportunities for learning conflict resolution, cooperation, empathy, and negotiation skills. Alternatively, unresolved conflicts or hostile relationships may hinder the development of these crucial social abilities. |
| 3. Psychological Development: | The psychological impact of sibling conflict is vast, affecting various aspects of an individual's overall development. Such conflicts can contribute to increased levels of aggression, lower self-esteem, and poorer mental health outcomes. Additionally, studies suggest that unresolved sibling conflicts may influence the formation of personal identity and contribute to the development of maladaptive behavioral patterns. |
| 4. Academic and Career Outcomes: | Exploring how sibling conflict influences academic performance and career outcomes sheds light on the long-term implications of these conflicts. Research indicates that prolonged and intense sibling conflicts can negatively affect academic motivation, achievement, and career aspirations. These conflicts may impede individuals' ability to focus, engage in productive relationships, and pursue their goals effectively. |
By examining the long-term effects of sibling conflict on emotional, social, psychological, and academic development, we gain a comprehensive understanding of its impact on individuals' lives. Recognizing these effects allows us to develop strategies and interventions to support healthy sibling relationships, promote positive development, and mitigate the potential negative consequences of such conflicts.
An exploration of how ongoing disagreements among siblings can mold individuals' emotional and interpersonal growth
In this section, we delve into the intricate dynamics of enduring disputes between family members, specifically focusing on brothers and sisters. By analyzing the ramifications of consistent conflicts, we aim to gain insights into the profound impact they can have on an individual's emotional well-being and their development of social skills.
Emotional Development: The continuous clashes within sibling relationships can shape an individual's emotional landscape in multifaceted ways. The intense interactions between brothers and sisters can contribute to the cultivation of various emotional responses, such as anger, frustration, and resentment. These persistent conflicts may also give rise to feelings of insecurity, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Through examining the emotional toll of ongoing disagreements, we aim to shed light on the long-term consequences they may exert on an individual's overall emotional development and mental health.
Social Development: Sibling conflicts can profoundly influence an individual's ability to navigate complex social interactions. The constant negotiation of power dynamics, the challenge of sharing resources, and the need to resolve conflicts within the sibling relationship provide a unique training ground for developing crucial social skills. However, ongoing conflict can also hinder the development of healthy communication patterns, empathy, and cooperation. By examining the intersection between persistent sibling disagreements and social development, we seek to gain a comprehensive understanding of how these conflicts shape individuals' interpersonal relationships beyond the familial sphere.
Note: While this section sheds light on the broader impacts of ongoing conflicts among siblings, it is important to acknowledge that every sibling relationship is unique and can manifest these effects to varying degrees.
Strategies for Resolving Sibling Conflict: Tools for Promoting Harmonious Relationships
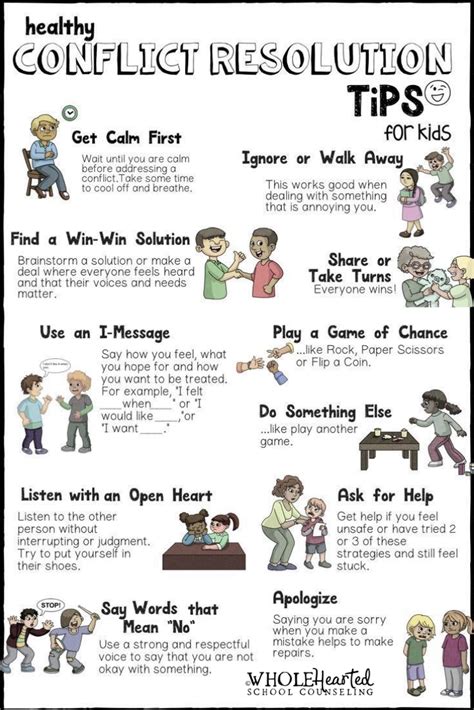
In this section, we will explore effective approaches for resolving disagreements and fostering positive interactions between brothers and sisters. By implementing these strategies, siblings can enhance their relationship by cultivating understanding, empathy, and cooperation.
1. Communication: Open and honest communication plays a crucial role in resolving conflict between siblings. Encouraging siblings to express their feelings and concerns, without judgment or interruption, creates an atmosphere of trust and understanding. Active listening and validating each other's perspectives can help reduce tension and promote effective problem-solving.
2. Negotiation and Compromise: Teaching siblings the art of negotiation and compromise can empower them to find mutually agreeable solutions. Encouraging them to identify their needs and interests and seek common ground can lead to win-win outcomes. Instilling the value of fair compromise helps siblings recognize the importance of finding middle ground and considering each other's preferences.
3. Conflict Resolution Skills: Equipping siblings with conflict resolution skills can provide them with the tools needed to navigate challenging situations. Teaching them techniques such as taking turns, finding alternatives, and brainstorming creative solutions fosters their ability to resolve conflicts independently. Additionally, emphasizing the importance of respect and empathy in conflict resolution can contribute to more peaceful and respectful interactions.
4. Strengthening Bonds: Activities that promote bonding and shared experiences can contribute to a stronger sibling relationship. Encouraging siblings to engage in cooperative tasks, such as playing team games or working on shared projects, can foster a sense of camaraderie and teamwork. Creating opportunities for positive interactions and shared interests can help cultivate a more harmonious relationship.
5. Parental Guidance and Mediation: Parents play a vital role in facilitating resolution of conflicts between siblings. Offering guidance and mediation when disputes arise can help siblings effectively communicate their needs and emotions. Parents can act as neutral mediators, encouraging open dialogue, and assisting in finding equitable solutions. By providing a supportive and nurturing environment, parents can empower siblings to work together towards resolving conflicts amicably.
By implementing these strategies, siblings can navigate conflict more effectively and build stronger and more harmonious relationships. Through open communication, negotiation, conflict resolution skills, strengthening bonds, and parental guidance, siblings can develop a foundation of respect and understanding, fostering lifelong connections with each other.
FAQ
Why do siblings fight so much?
Siblings often fight because they are competing for attention, resources, or parental approval. They may also fight due to jealousy or differences in personality and interests.
What can parents do to reduce conflicts between siblings?
Parents can promote positive sibling relationships by setting clear expectations for behavior, encouraging communication and compromise, providing individual attention to each child, and teaching conflict resolution skills.
Are sibling conflicts harmful in the long run?
Sibling conflicts are a normal part of development and can actually help children develop important social and emotional skills. However, persistent and severe conflicts may have negative effects on sibling relationships and overall well-being.
Can sibling conflicts be a reflection of larger family dynamics?
Yes, sibling conflicts can often reflect larger family dynamics. If parents frequently engage in conflicts or show favoritism towards certain children, it can contribute to increased conflicts between siblings.



