In the depths of the natural world lies a truly captivating and enigmatic phenomenon that has fascinated mankind for centuries. It is a marvel that remains largely untouched by human intervention, yet its intricate system has left scientists and researchers awe-inspired. Delve into the realm of these small creatures that have been intricately woven into the fabric of our environment – the honeybees.
Diving deep into the realm of these incredible insects unveils a mesmerizing web of interconnections and symbiotic relationships. As the buzzing sound of their delicate wings fills the air, an intricate dance unfolds as they tirelessly gather nectar and pollen, transferring life from flower to flower. This intricate pollination process not only sustains the honeybee colonies but also shapes the very landscapes we inhabit.
The honeybees, nature's industrious workers, have long been revered for their exceptional social structure and remarkable intelligence. Inside their hive, myriad roles are assigned, each bee diligently playing their part to ensure the survival of the collective. From the mighty queen, laying thousands of eggs a day, to the diligent worker bees that tirelessly forage for food, their teamwork and specialization showcase the true marvels of nature's design.
Beneath the veil of their buzzing perfection lies a secret treasure – the golden elixir of life, honey. This precious substance, painstakingly produced by honeybees using floral nectar, has entranced humans for millennia. Its divine sweetness and numerous medicinal qualities have given honey a revered status throughout history, making it not just a treat for our taste buds but a revered elixir for our well-being.
Join us on a journey into this extraordinary world as we uncover the hidden wonders of the honeybee. Together, let us unlock the secrets of their intricate social structure, their impressive communication methods, and the captivating process of transforming nectar into liquid gold – a testament to the exceptional harmony and ingenuity found within nature itself.
The Vital Role of Honey Bees in Our Ecosystem

In today's world, where the intricate workings of nature are often overlooked, one species stands out as a truly essential contributor to our ecosystem - the honey bees. These remarkable creatures play an indispensable role in pollination, biodiversity, and food production, making them vital for the balance and sustainability of our environment.
Without honey bees, the diversity and abundance of flowering plants would drastically decline, affecting countless other species that rely on these plants for food and shelter. Pollination, the transfer of pollen from the male to the female reproductive organs of flowers, is a critical step in the reproductive process of plants. As honey bees visit flowers in search of nectar and pollen, they inadvertently pick up and deposit pollen grains, allowing for successful fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits.
Furthermore, honey bees contribute to biodiversity by creating and maintaining habitats through their intricate construction of beehives. These hives provide shelter for the colony, as well as nesting sites for numerous other insect species. The activities of honey bees also contribute to the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients in the environment.
When it comes to food production, honey bees have a significant impact. They are responsible for pollinating a large portion of the crops that humans rely on for sustenance, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds. In fact, it is estimated that honey bees contribute to the pollination of approximately one-third of the world's food crops. Without their diligent work, many crops would suffer reduced yields or fail to produce viable seeds, leading to potential food shortages and economic consequences.
Despite their crucial role, honey bees face numerous challenges, including habitat loss, pesticide exposure, climate change, and diseases. The decline in honey bee populations has alarming implications for our ecosystem, as well as for agricultural productivity and food security. It is therefore imperative that we recognize the importance of honey bees and take action to protect and support their populations.
In conclusion, honey bees are not just insects buzzing around flowers; they are indispensable contributors to our ecosystem. Their role in pollination, biodiversity, and food production cannot be overstated. By understanding and valuing the vital work of honey bees, we can take steps to ensure their well-being and safeguard the delicate balance of nature.
The Enigmatic World Inside a Beehive
Within the depths of a buzzing sanctuary lies a mesmerizing realm of activity, a microcosm teeming with life and purpose. Deep within the confines of a hive, bees embark on an intricate dance, driven by their innate instincts and the collective intelligence that governs their every move. The complex organization, hierarchical structure, and remarkable harmony of these tiny inhabitants create an intriguing and captivating world that remains largely hidden from our everyday lives.
- Enigmatic Communication: Inside the hive, bees engage in a fascinating form of communication, utilizing intricate scent cues, vibrations, and precise maneuvers to convey detailed information to their fellow comrades. Through this intricate web of signals, they effectively coordinate their activities, ensuring the smooth functioning of their community.
- Social Hierarchy: Similar to a finely orchestrated symphony, a bee society operates under a meticulously defined social order. From the lowly workers, faithfully tending to the hive's needs, to the diligent nurses, dutifully nourishing the young brood, to the esteemed queen who reigns supreme, each member plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the colony.
- The Hive's Architecture: The construction of a beehive is a remarkable feat of engineering. Bees exhibit astonishing architectural skills as they meticulously craft hexagonal honeycomb cells, maximizing space and efficiency. This architectural marvel serves not only as a nursery for the developing brood but also as a storage facility for their precious food reserves.
- The Dance of Pollination: Operating as nature's diligent gardeners, bees play a critical role in pollination, enabling the proliferation of blooming flora. Within the hive, scouts embark on exploratory journeys, diligently searching for nectar-laden flowers. Upon their return, they mesmerizingly communicate the location of these floral treasures through a unique waggle dance, guiding their fellow foragers to abundant sources of sustenance.
- The Secret Life of Drones: Amidst the order and industry of the hive, drones exist as enigmatic and ephemeral figures. Their presence is limited, their main purpose being to mate with the queen before their ultimate demise. Despite their seemingly insignificant role, drones play a crucial part in preserving genetic diversity and ensuring the colony's survival.
Behind the delicate façade of a beehive lies a captivating world governed by intricate mechanisms and astonishing behaviors. Through a deeper understanding of the inner workings of these industrious insects, we can unlock a wealth of knowledge and inspiration, unraveling the mysteries that surround the fascinating world inside a bee hive.
The Life Cycle of Apis Mellifera: From Egg to Adult
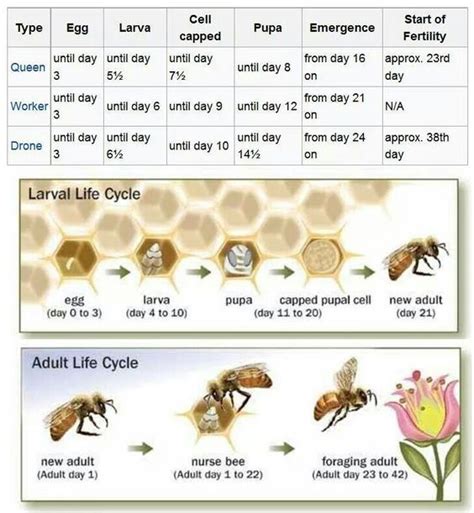
Understanding the journey of a honey bee from its initial stage as an egg to its final transformation into an adult is a fascinating exploration into the intricate cycle of nature's most prized pollinators. This section will delve into the various stages of development that shape the life of Apis Mellifera, highlighting the remarkable adaptations and evolutions that occur at each step.
| Stage | Description | Durations |
|---|---|---|
| Egg | The life cycle of a honey bee begins with a small, whitish egg laid by the queen bee. These eggs are packed with potential, holding the genetic blueprint for the individual bee's future. | 3 days |
| Larva | From the egg hatches the larva, a legless, grub-like creature that is nurtured by nurse bees with royal jelly. The larva grows rapidly, molting its skin several times, and consuming copious amounts of food to fuel its growth. | 5-6 days |
| Pupa | After the larval stage, the bee enters the pupal stage, during which it undergoes a remarkable transformation. Encased within a protective cocoon, the organism gradually changes its form, developing fully-functioning body parts and transitioning into an adult bee. | 12-14 days |
| Adult | Emerging from the cocoon, the adult honey bee breaks free and enters the world of the hive as a young adult. It starts its life by assuming various roles within the colony, such as tending to brood, cleaning the hive, and eventually, foraging for nectar and pollen. | Varies (up to several months) |
The life cycle of honey bees is a captivating process that exemplifies nature's intricate design. The stages of development from egg to adult offer insights into the remarkable transformations and unique adaptations that allow honey bees to thrive and contribute to the delicate balance of ecosystems.
The Dance Language of Bees: Communication for Success
In the realm of honey bees, communication holds the key to their thriving colonies and efficient foraging activities. Through a fascinating dance language, these diligent insects convey important information to their fellow hive-mates, enabling them to navigate and locate valuable resources in their surrounding environment. The intricate communication system employed by honey bees showcases their remarkable ability to effectively communicate complex information and ensure the success of their cooperative endeavors.
The Dance Floor as a Communication Stage
The dance language of honey bees involves precise movements and patterns performed on the honeycomb, serving as a visual communication platform within the hive. By performing specific dances, bees are able to convey vital information such as the direction, distance, and quality of nectar sources or potential new hive locations. Each dance is tailored to relay specific details, ensuring accurate communication and aiding in the collective decision-making process.
Decoding the Waggle Dance
The most renowned dance form within the honey bee repertoire is the waggle dance, performed by forager bees to communicate the location of food sources. This elaborate dance involves intricate figure-eight patterns, with the direction and duration of the waggle providing crucial information to other bees. By analyzing the angle of the waggle in relation to the vertical axis of the honeycomb, as well as the duration of the dance, fellow bees are able to determine both the direction and distance to the food source, allowing for efficient resource exploitation.
Round Dance: A Call for Nearby Resources
In addition to the waggle dance, honey bees also utilize the round dance to communicate the presence of nearby nectar sources. This simple yet effective dance involves a circular motion performed by forager bees on the honeycomb. By engaging in this dance, bees signal the proximity of resources, allowing other workers to promptly locate and exploit these opportunities close to the hive.
In conclusion, the dance language of honey bees serves as a sophisticated system for effective communication and coordination within the hive. Through precise movements and patterns, bees are able to convey crucial information about food sources and potential new hive locations, ensuring the success of their foraging endeavors and the overall prosperity of the colony.
The Enigmatic Phenomenon of Colony Collapse Disorder
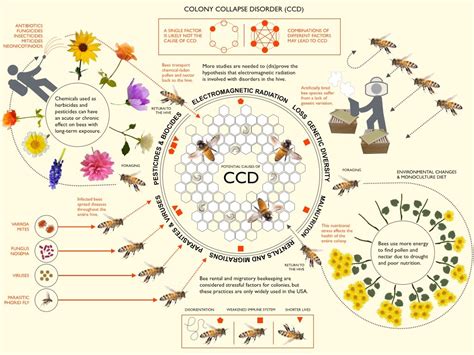
In the realm of beekeeping, a perplexing and puzzling occurrence has been captivating the minds of researchers and honeybee enthusiasts alike – Colony Collapse Disorder. This enigmatic phenomenon has garnered substantial attention due to its devastating impact on honeybee colonies worldwide. Despite extensive research and meticulous observation, the precise cause of Colony Collapse Disorder remains elusive, hiding behind a shroud of mystery and intrigue.
Colony Collapse Disorder refers to a disturbing phenomenon in which entire honeybee colonies abruptly and inexplicably collapse, leaving behind vast numbers of dead bees and a deserted hive. What makes this affliction truly confounding is the absence of clear-cut reasons behind the collapse. Symptoms of Colony Collapse Disorder include the abrupt disappearance of adult bees, the absence of dead honeybees around the hive, and a distinct scarcity of food stores.
Researchers have proposed a myriad of potential factors that could contribute to the incidence of Colony Collapse Disorder. These encompass both natural and human-made stressors, including the spread of infections and parasites, exposure to pesticides and chemicals, inadequate nutrition, and climate change. However, no single causative agent has been definitively identified, making the disorder even more enigmatic.
The consequences of Colony Collapse Disorder are far-reaching and impact not only honeybee populations but also ecosystems and agricultural systems worldwide. Honeybees play a vital role in pollinating numerous plant species, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Their decline threatens biodiversity and jeopardizes the global food supply chain. Understanding and unraveling the mysteries surrounding Colony Collapse Disorder is therefore of paramount importance.
Efforts to overcome the challenges posed by Colony Collapse Disorder require multifaceted approaches, from implementing sustainable agricultural practices to reducing pesticide use and enhancing honeybee health management. Continued research and collaboration among scientists, beekeepers, and policymakers are essential to unlocking the secrets behind this puzzling phenomenon and ensuring the survival of honeybee populations for generations to come.
The Remarkable Advantages of Honey: Nature's Most Delicious Present
In this section, we will explore the exceptional perks that come with indulging in the delectable substance known as honey. Discover the myriad ways in which honey can enhance your well-being, captivate your taste buds, and contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
1. A Natural Energy Booster
One of the remarkable attributes of honey lies in its ability to provide a natural and sustainable source of energy. Its unique composition, filled with natural sugars and carbohydrates, makes it an ideal fuel for your body to function optimally throughout the day. Unlike artificial sweeteners or refined sugars, honey offers a slow yet steady release of energy, preventing sudden spikes and crashes.
2. A Potent Antioxidant Powerhouse
Another remarkable benefit of honey is its high antioxidant content. Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful free radicals that can cause oxidative stress and damage to our cells. Regular consumption of honey can contribute to a strengthened immune system, improved skin health, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
3. An Effective Natural Remedy
Honey has been revered for centuries for its medicinal properties, making it a versatile natural remedy. Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties make it effective in soothing sore throats, treating wounds, and alleviating digestive issues. Incorporating honey into your daily routine can offer relief from common ailments and promote overall well-being.
4. An Exceptional Culinary Ingredient
Beyond its numerous health benefits, honey adds a delightful touch to various culinary creations. Whether drizzled over a bowl of fresh fruits, used as a natural sweetener in recipes, or savored as a spread on warm toast, honey brings a unique and delicious flavor profile to a wide array of dishes. Its versatility in the kitchen makes it a must-have ingredient for both amateur cooks and professional chefs alike.
5. An All-Natural Beauty Aid
While honey's benefits are not limited to consumption, its properties extend to the realm of skincare as well. Its antibacterial and moisturizing properties make it a popular ingredient in natural beauty products. From face masks to hair treatments, honey can help nurture and revitalize your skin and hair, leaving you with a healthy and radiant glow.
In conclusion, honey truly stands out as a precious gift from nature, offering not only its delicate sweetness but also a wide range of extraordinary advantages. Incorporating honey into your life can provide you with a host of health benefits, culinary delights, natural remedies, and beautifying effects, ensuring that you fully savor nature's most delightful creation.
Beekeeping Techniques: Nurturing and Safeguarding the Honey Bee Population

In this section, we will explore various methods and strategies for fostering the growth and protection of the invaluable honey bee population. Discovering effective techniques and practices is crucial to ensure the well-being and sustainability of these vital pollinators.
- Promoting Bee-Friendly Landscapes: Creating diverse and pesticide-free environments that provide an abundance of flowering plants and trees for bees to forage on can significantly support their populations.
- Constructing Proper Hive Structures: Building suitable beehives with well-designed frames, entrance reducers, and ventilation systems can help maintain optimal living conditions for honey bees.
- Implementing Integrated Pest Management: Adopting holistic approaches to pest control, such as monitoring hive health regularly and utilizing natural remedies, can reduce the impact of parasites and diseases on bee colonies.
- Utilizing Sustainable Beekeeping Practices: Following ethical beekeeping methods, including responsible honey extraction, swarm prevention, and careful handling of bees, ensures the overall well-being and longevity of the honey bee population.
- Supporting Research and Education: Investing in scientific studies and educational programs focused on honey bee health and conservation enables the dissemination of knowledge and the development of innovative techniques to protect honey bees.
- Encouraging Collaboration and Partnerships: Facilitating cooperation among beekeepers, farmers, researchers, and policymakers can foster a collective effort to address the challenges faced by honey bees and find sustainable solutions together.
By implementing these beekeeping techniques, individuals and communities can contribute to nurturing and safeguarding the honey bee population and ensuring the continued pollination services they provide for the health of our ecosystems and agricultural practices.
FAQ
Why are honey bees so important for our ecosystem?
Honey bees play a crucial role in pollinating flowering plants, which allows these plants to reproduce and produce fruits and seeds. About one-third of the global food supply depends on pollinators like honey bees.
How do honey bees collect nectar and convert it into honey?
Honey bees collect nectar by visiting flowers and using their long tongues to suck the sweet liquid. The nectar is then stored in a special honey stomach. Once back at the hive, the bees regurgitate the nectar and pass it to other worker bees. Through a process of evaporation and enzymatic activity, the nectar gradually transforms into honey.
What makes honey so special and beneficial to health?
Honey is not just a natural sweetener; it also offers numerous health benefits. It contains various antioxidants and antibacterial properties, which can help boost the immune system and soothe coughs and sore throats. Additionally, honey has been used in traditional medicine for its wound-healing properties.
Why are honey bees facing population decline?
Honey bees are facing population decline due to various factors, including loss of habitat, pesticide use, pests and diseases, climate change, and changes in agricultural practices. These factors affect the bees' ability to find food, weaken their immune systems, and disrupt their reproductive cycles, leading to colony losses.
What can individuals do to support honey bee conservation?
There are several actions individuals can take to support honey bee conservation. Planting bee-friendly flowers and avoiding pesticide use in gardens can provide bees with a source of food and a safe habitat. Supporting local beekeepers by buying their honey and beeswax products can also contribute to the sustainability of honey bee populations.
How do honey bees produce honey?
Honey bees produce honey by collecting nectar from flowers. They collect nectar using their long tongues, then store it in a special stomach called the honey stomach. Once the honey stomach is full, the bee returns to the hive and regurgitates the nectar into the mouth of another bee. This process is repeated until the nectar is partially digested and transformed into honey. The bees then deposit the honey into the honeycomb cells, where it is further dehydrated until it reaches the desired consistency.



