In our ever-evolving world, our minds are constantly occupied by the mysterious complexities of the human psyche. Among the labyrinth of thoughts and desires that shape our existence, one unrelenting inclination emerges time and again: the relentless pursuit of indulgence. This insatiable craving, deeply ingrained within our beings, manifests itself in myriad ways, yet none quite as incessantly as our yearning for sustenance.
Unbeknownst to us, our souls are haunted by an enigmatic force, a driving force that compels us to seek nourishment at every turn. As we navigate the tumultuous landscapes of our dreams, the tantalizing aroma of desires waft through the corridors of our subconscious minds, awakening our senses and catapulting us into a realm where culinary pleasures reign supreme.
With each passing day, our minds become a battleground between the rationality of moderation and the unruly tide of our relentless appetites. We find ourselves oscillating between the fragile fragility of self-control and the tempestuous torrents of temptation. It is in these moments, when our resilience is inevitably tested, that we come to question the nature of our existence as insatiable beings.
Yet, as perplexing as these desires may be, they hold a mirror to the depths of our humanity. They remind us of our vulnerabilities, of our inherent need for sustenance, and of the profound connection between our physical bodies and the cravings that reside within. They capture the eternal struggle between our conscious will and the untamed yearnings that reside in the depth of our souls.
The Psychological Fascination with Food: Uncovering the Mysteries of Our Insatiable Cravings

The human mind has long been captivated by the intricacies of our relationship with food. From the profound influence it holds over our emotions to the curious patterns of our insatiable appetites, the psychological fascination with food has sparked a quest to understand the mysteries behind our endless cravings.
Delving into the realm of psychology, researchers have sought to unravel the complex web of factors that contribute to our everlasting hunger. This exploration has led to a deeper understanding of the cognitive, emotional, and biological mechanisms that drive our relentless desire for nourishment.
Examining the psychological aspects of food consumption reveals a multifaceted tapestry of influences. From the subconscious associations we form with particular foods to the powerful impact of social and cultural factors on our dietary choices, the complexities of our relationship with food are far-reaching and often intriguing.
- Emotional Eating: Unveiling the Role of Food in Comfort and Stress Relief
- The Power of Advertising: How Marketing Tactics Shape Our Cravings
- Craving and Dopamine: The Neurotransmitter Connection to Our Unquenchable Desires
- Food and Memory: Unraveling the Intricate Link Between Taste and Past Experiences
- The Social Dynamics of Eating: Exploring the Influence of Peers and Social Settings
By exploring the psychological fascination with food, we gain insight into the complexities of our own minds and behaviors. Through this understanding, we may uncover strategies to navigate our insatiable cravings and establish a healthier, more balanced relationship with the sustenance that fuels our bodies and minds.
Unveiling the Science Behind Insatiable Cravings: Unraveling the Intricate Mechanisms of Hunger
Delving into the depths of our insatiable appetites, this section aims to shed light on the complex scientific factors that drive our cravings. By examining the multifaceted mechanisms that govern hunger, we can gain a deeper understanding of why our appetites seem unquenchable and how they influence our daily lives.
The Surprising Role of Hormones:
One of the key players in the intricate web of hunger regulation are hormones. These powerful substances act as messengers within our bodies, relaying information to our brains about the status of our energy stores. By affecting our hunger levels and satiety, hormones such as ghrelin and leptin play a vital role in the endless cycle of cravings that we experience.
The Power of Brain Chemistry:
Delving into the neural intricacies of our appetite control, this section focuses on the role of neurotransmitters and brain regions. Serotonin, dopamine, and endorphins are just a few of the chemical messengers within our brains that directly impact our cravings and urge to eat. We will explore how imbalances in these neurotransmitters can lead to a perpetuating cycle of overeating and its potential implications.
Environmental and Emotional Triggers:
Beyond the physiological aspects, our environment and emotions also play a significant role in our insatiable appetites. The influence of external cues, such as food advertisements and availability, can stimulate our cravings and lead us to consume more than what our bodies actually need. Likewise, emotions, stress, and psychological factors can drive us to seek comfort or distraction in food, perpetuating our endless cycle of eating.
The Role of Genetics and Evolution:
Within the intricate tapestry of our genetic makeup lie clues about our unquenchable appetites. By examining the evolutionary origins of our cravings and their potential genetic underpinnings, we can begin to unravel the reasons behind our constant desires for food. This section explores the fascinating interplay between our genes and our insatiable appetites.
Unraveling the Mind-Body Connection:
A deeper understanding of the mind-body connection and its influence on our appetites offers insights into how our thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes towards food impact our eating patterns. By exploring the concept of mindful eating and examining the power of positive psychology in curbing our endless appetites, we can gain valuable tools for achieving greater control over our cravings.
In conclusion, by delving into the intricacies of the science behind our unquenchable appetites, we can gain a deeper understanding of the physiological, neurological, environmental, and psychological influences that contribute to our constant desire for food. Armed with this knowledge, we can strive to find a balance between satisfying our appetites and maintaining a healthy relationship with food.
Understanding the Psychological & Emotional Factors Behind Overeating

The journey from seeking comfort through food to indulging in binge eating can be influenced by a myriad of psychological and emotional factors. Exploring the intricate web of thought processes and feelings that drive our constant need for food can provide valuable insights into the roots of our overeating habits.
One of the key psychological factors behind overeating is the phenomenon of emotional eating, where individuals turn to food as a means of soothing or coping with their emotions. Instead of addressing and processing emotions in a healthy manner, the act of eating becomes a substitute for emotional fulfillment. Stress, sadness, loneliness, or even boredom can trigger this pattern of behavior, giving rise to a continuous cycle of seeking comfort through food.
Furthermore, societal and cultural pressures can also play a significant role in driving our constant need for food. The pervasive influence of advertising, social media, and peer pressure to conform to certain body standards can lead to body dissatisfaction and low self-esteem. In an attempt to manage these negative emotions, individuals may turn to food as both a source of distraction and a way to provide temporary pleasure and relief.
Additionally, our unique personal histories and experiences shape our relationship with food and eating. Traumatic events, negative childhood experiences, or the development of unhealthy coping mechanisms can all contribute to the development of binge eating behaviors. The act of overeating may serve as a form of self-soothing or a way to regain a sense of control, providing temporary relief from underlying emotional pain.
Recognizing and addressing the psychological and emotional factors that drive our constant need for food can pave the way for developing healthier coping mechanisms and finding alternative sources of emotional fulfillment. By understanding the complexity of our relationship with food, we can work towards creating a more balanced and sustainable approach to eating, ensuring a healthier lifestyle both physically and mentally.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| - Psychological factors, such as emotional eating, contribute to our constant need for food |
| - Societal and cultural pressures can influence our relationship with food |
| - Personal experiences and traumas may contribute to binge eating behaviors |
| - Recognizing these factors can lead to healthier coping mechanisms and emotional fulfillment |
The Influence of Genetics on Insatiable Hunger: Shedding Light on Our Unyielding Cravings
Within the realm of our insatiable cravings lies a hidden culprit that may ultimately be responsible for our overwhelming desire for more food: our genetic makeup. While it may be tempting to assign blame solely to our lack of willpower or societal influences, an emerging body of research suggests that our DNA plays a significant role in shaping our seemingly endless appetites.
Our genetic code serves as a blueprint for various traits and characteristics, and recent studies have begun to unravel the complex interplay between specific genes and our propensity for constant eating. These genetic factors can influence our metabolism, the release of certain hunger-related hormones, and even our brain's reward system, ultimately driving us to seek out more food even when we are satiated.
| Key Genetic Factors Affecting Our Endless Appetites | |
|---|---|
| 1. FTO Gene | The FTO gene, also known as the "fat mass and obesity-associated gene," has been extensively studied for its role in regulating appetite and energy balance. Variations in this gene have been linked to an increased risk of obesity and a heightened desire for calorie-dense foods. |
| 2. MC4R Gene | The MC4R gene is involved in the regulation of hunger and satiety signals in the brain. Mutations in this gene can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to a diminished sense of fullness and an increased drive to consume more food. |
| 3. Leptin Gene | The leptin gene codes for the hormone leptin, which plays a crucial role in appetite regulation. Deficiencies in this hormone or impaired receptors can result in a constant state of hunger, as the brain fails to receive the signal indicating that we have consumed enough food. |
While these are just a few examples, they highlight the growing body of evidence suggesting a strong genetic component to our insatiable appetites. However, it is important to note that genetics alone do not determine our eating behavior. Environmental factors, such as diet, exercise habits, and cultural influences, also play a significant role in shaping our relationship with food.
Understanding the influence of genetics on our endless appetites can provide valuable insights into the development of targeted interventions and personalized approaches to help individuals manage their cravings and maintain a healthy relationship with food. By unraveling the intricate mechanisms behind our insatiable hunger, we can ultimately shift the conversation away from blame and towards a better understanding of the complex factors that contribute to our insatiable desire for more.
Unveiling the Power of Food Marketing: Exploring the Influence of Advertising & Media on Our Insatiable Cravings

In this section, we delve into the captivating world of food marketing and its profound impact on our insatiable desire for food. Through an examination of advertising and media, we seek to unravel the intricate web of influences that incite an endless craving for food, ultimately shaping our eating habits and preferences.
The Allure of Food Advertising:
Food advertisements saturate every aspect of our lives, bombarding us with tantalizing images, catchy slogans, and alluring promises. These marketing strategies seamlessly integrate into our daily routines, triggering strong emotional responses and cravings. The allure of food advertising lies in its ability to tap into our deepest desires, creating an insatiable urge to indulge, regardless of our actual hunger.
The Role of Media in Shaping Appetites:
From television shows to social media influencers, the media plays a crucial role in shaping our appetites. Through carefully curated content, these platforms normalize excessive consumption and glorify certain food habits. The constant exposure to indulgent food imagery perpetuates a culture of overeating and fosters unrealistic expectations around food, leading to a constant desire for more.
The Science of Persuasion:
Food marketers employ various psychological techniques to tap into our subconscious desires, making their products irresistible. From vivid and colorful visuals to persuasive language and endorsements, these strategies manipulate our senses and emotions, igniting cravings that are difficult to resist. Understanding the science behind these methods allows us to unravel the power they hold over our constant desire for food.
Unintended Consequences:
While food marketing may seem harmless on the surface, the consequences of its influence on our constant desire for food can be severe. Unhealthy eating patterns, obesity, and other diet-related health issues are on the rise, partially attributed to the manipulation tactics employed by food marketing. Acknowledging and addressing these unintended consequences is crucial for promoting healthier relationships with food.
By unraveling the power of food marketing and media, we can gain a deeper understanding of our constantly evolving cravings. Through awareness and critical thinking, we can begin to challenge these influences and build a healthier, more balanced relationship with food.
The Influence of Societal Expectations on Overeating
In this section, we will explore how cultural norms and social expectations play a significant role in contributing to our insatiable hunger and excessive food consumption.
One cannot deny the impact of cultural norms on our eating habits. From childhood, we are often taught that finishing a plate of food is a sign of respect and gratitude towards the cook. This ingrained belief encourages us to consume more than our bodies actually need, leading to overeating.
Social expectations also come into play when it comes to our endless appetites. Whether it is a family gathering, a celebration, or a social event, there is an implicit pressure to indulge in large quantities of food. This pressure to conform to societal norms drives us to eat beyond our hunger levels, fueling our never-ending desire for food.
Moreover, advertising and media further perpetuate these societal expectations. The constant bombardment of images and messages promoting abundant food consumption as a symbol of happiness and success creates a psychological association between overeating and positive emotions. As a result, we find ourselves constantly craving and succumbing to our insatiable appetites.
Furthermore, the availability and accessibility of food in our modern society contribute to the problem. From fast food chains on every corner to 24/7 convenience stores, we are surrounded by opportunities to indulge in our food desires. The convenience and abundance of food options make it easy for us to give in to the societal pressure to overeat.
| Factors Influencing Overeating: |
|---|
| Cultural norms |
| Social expectations |
| Advertising and media influence |
| Availability and accessibility of food |
In conclusion, our never-ending appetites can be attributed, at least in part, to the societal pressure to overeat. Cultural norms, social expectations, advertising, and accessibility to food all contribute to our insatiable hunger and excessive food consumption. Understanding these influences can help us navigate and make healthier choices in a world where endless eating seems to be the norm.
The Evolutionary Origins of Our Insatiable Cravings: Unveiling the Roots of Endless Hunger

In this section, we delve into the deep-seated origins of our insatiable cravings, exploring the evolutionary factors that have shaped our never-ending hunger. By tracing back the roots of our endless appetites, we gain valuable insight into the driving forces behind our constant desire to consume.
- Survival Instincts: Our insatiable craving for food can be attributed to our primal survival instincts. Throughout evolution, humans have been hardwired to seek out and consume food to ensure their survival. Our ancestors faced periods of scarcity and uncertainty, which led to the development of a robust appetite to store energy during times of abundance.
- Energy Conservation: Another contributing factor to our endless hunger lies in our body's constant need for energy. As complex organisms, we require a substantial amount of energy to sustain our bodily functions and carry out daily activities. This biological necessity has driven us to develop insatiable cravings to ensure an adequate energy supply is maintained.
- Food Availability: The availability and accessibility of food have played a significant role in shaping our insatiable appetites. In earlier times, when food was not as readily available as it is today, the opportunity to indulge in abundant resources was rare. Consequently, humans developed a heightened desire to consume whenever an opportunity presented itself, leading to our enduring craving for more.
- Reward System: Our brain's reward system also contributes to the persistence of our endless hunger. Consuming food triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This physiological response reinforces our desire for consumption, creating a cycle that perpetuates our insatiable cravings.
- Social and Cultural Influences: Additionally, our insatiable hunger is influenced by social and cultural factors. Over time, food has become intertwined with various aspects of human life, such as celebrations and social gatherings. These societal norms and traditions further strengthen our desire to indulge, making our cravings even more difficult to satiate.
By understanding the evolutionary roots of our insatiable cravings, we can gain a deeper appreciation for our complex relationship with food. It allows us to recognize that our constant desire for sustenance is not merely a personal flaw, but a result of thousands of years of evolutionary development.
Food Addiction: Is It Real? Understanding the Controversial Concept of Being Addicted to Food
Exploring the contentious notion of being addicted to food, this section delves into the ongoing debate surrounding food addiction and its validity as a legitimate condition. Despite the absence of an universally agreed-upon definition, the concept of food addiction continues to generate significant discussion and research.
Some argue that food addiction shares common features with substance addictions, such as tolerance, withdrawal, and cravings. They believe that certain types of food, particularly those high in sugar, fat, and salt, can activate reward centers in the brain and lead to addictive-like behaviors. On the other hand, skeptics question the classification of food addiction, emphasizing the fundamental biological need for nourishment and the absence of substances in food that directly alter brain chemistry.
A crucial aspect of understanding food addiction is recognizing the potential contributing factors. Factors such as genetics, environment, and psychological influences may all play a role in the development and maintenance of addictive-like eating patterns. Additionally, emotional factors, such as stress or trauma, are often intertwined with food addiction and can serve as triggers for consuming palatable but nutritionally poor foods.
| Pros of Recognizing Food Addiction | Cons of Recognizing Food Addiction |
|---|---|
| 1. Increased awareness and understanding of the complexity of overeating behaviors | 1. Potential stigmatization of individuals struggling with unhealthy eating habits |
| 2. Development of tailored interventions and treatment options | 2. Difficulty in establishing clear diagnostic criteria |
| 3. Identification of specific food triggers to support healthier eating habits | 3. Potential tendency to overlook societal factors contributing to overeating |
While debates surrounding the notion of food addiction continue, it is essential to approach the topic with an open mind and recognize the potential implications of classifying food addiction as a recognized condition. By understanding the various perspectives on this controversial concept, we can strive to enhance our comprehension of the complex relationship between individuals and food.
The Role of Stress & Emotional Eating in Our Insatiable Hunger: Unveiling the Link Between Mood and Food
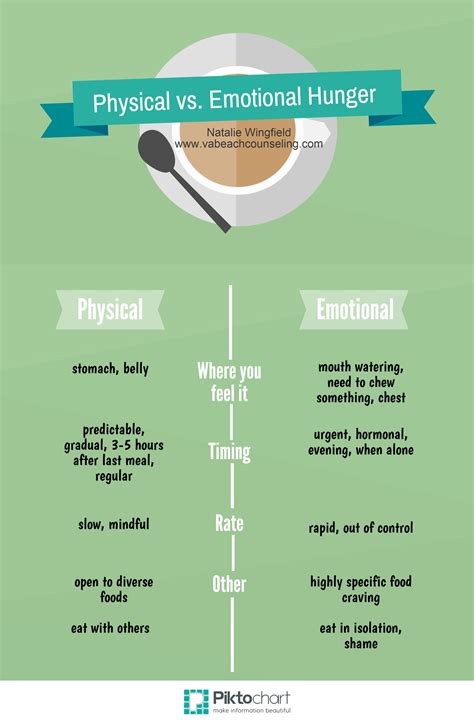
When it comes to our unending cravings and insatiable hunger, stress and emotional eating play a significant role in driving our voracious appetites. This section will delve into the intricate connection between our emotional state and the way we turn to food to seek comfort, escape, or cope with stressful situations. By unraveling this complex association, we can gain a deeper understanding of how our mood influences our eating habits.
Stress has become an inherent part of our modern lives, impacting our physical and mental well-being. Many individuals find solace in turning to food as a coping mechanism when faced with stressors. The overarching desire for comfort often leads to mindless or excessive eating, as we attempt to find temporary relief from our emotional distress. This emotional connection to food is deeply rooted in our subconscious, making it challenging to break the cycle of stress-induced eating.
Moreover, emotional eating further exacerbates our endless appetites. The correlation between our mood and food consumption is undeniable. When we experience negative emotions such as sadness, loneliness, or anxiety, we tend to gravitate towards certain types of food, typically high in sugar, fat, or salt. These foods trigger the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, providing a brief moment of respite from our emotional turmoil.
Understanding the mechanisms at play when stress and emotions intersect with our eating habits is crucial in combating our incessant hunger. By recognizing the triggers that lead to emotional eating, we can begin to develop healthier coping strategies and break free from the cycle of using food as a source of comfort. This newfound awareness empowers individuals to adopt mindfulness techniques, seek social support, or find alternative stress-relieving activities, ultimately reducing the endless cravings and restoring a more balanced relationship with food.
Strategies for Managing Our Constant Cravings: Practical Tips and Techniques to Tame Our Insatiable Desires
When it comes to our insatiable appetites, finding effective strategies for managing and controlling our constant cravings can be crucial. In this section, we will explore various practical tips and techniques that can help us gain control over our overwhelming desire for food, without resorting to extreme measures or deprivation.
1. Mindful Eating
One powerful strategy for managing our constant cravings is practicing mindful eating. This involves fully engaging our senses and being present in the moment while enjoying our meals. By paying attention to the flavors, textures, and smells of our food, we can enhance the overall satisfaction and reduce the urge to constantly indulge. Incorporating mindful eating techniques, such as chewing slowly and savoring each bite, can help us become more attuned to our body's signals of hunger and fullness, leading to more balanced and controlled eating habits.
2. Portion Control
Another effective technique for taming our insatiable appetites is implementing portion control strategies. By consciously monitoring and limiting the amount of food we consume, we can still enjoy our favorite dishes without overindulging. Using smaller plates and bowls, pre-portioning snacks into smaller containers, and being mindful of serving sizes can help us maintain a healthier relationship with food and prevent constant overeating.
3. Balanced Meals
Ensuring that our meals are nutritionally balanced is essential for managing our constant cravings. Including a combination of protein, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates in each meal can promote satiety and reduce the urge to constantly seek out snacks. Additionally, incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables can provide important micronutrients while adding flavor and visual appeal to our plates, making our meals more satisfying and enjoyable.
4. Healthy Snack Options
Having a selection of healthy snack options readily available can also be a valuable tool for taming our insatiable appetites. When cravings strike, having nutritious alternatives such as fresh fruits, vegetables with dip, or a handful of nuts can help satisfy our hunger while avoiding unhealthy indulgences. Planning and preparing these snacks ahead of time can ensure that we always have a satisfying and nourishing option within reach.
5. Stress Management
Managing stress is essential in curbing our constant cravings. Stress can disrupt our hormones and lead to emotional eating or an increased desire for comfort foods. Finding healthy coping mechanisms to deal with stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in physical activity, or seeking support from loved ones, can help us address the root causes of our insatiable appetites and prevent them from spiraling out of control.
6. Seeking Support
Finally, seeking support from professionals or joining a community of individuals with similar struggles can provide invaluable assistance in managing our constant cravings. Working with a registered dietitian, therapist, or attending support groups can offer guidance, accountability, and insights into addressing the underlying factors contributing to our insatiable appetites.
By implementing these practical tips and techniques, we can develop healthier eating habits and gain control over our constant cravings, ultimately leading to a more balanced and satisfying relationship with food.
FAQ
What are some common reasons why people dream about constantly eating?
There are several common reasons why people may dream about constantly eating. One reason could be that they have strong cravings or a desire for certain foods. Another reason could be that they feel a sense of never being satisfied in their waking life, which manifests as a constant desire to eat in their dreams. Additionally, constant eating dreams can sometimes be a reflection of emotional or psychological issues, such as stress, anxiety, or feelings of emptiness.
Is it normal to have dreams where I am eating all the time?
Yes, it is normal to have dreams where you are constantly eating. Dreams can often be a reflection of our thoughts, desires, and experiences, and food is a basic human need. So, dreaming about eating frequently could simply be your brain processing your hunger or desire for certain foods. However, if you find that these dreams are becoming excessive or affecting your daily life, it may be worth discussing with a healthcare professional.
Can constant eating dreams be a sign of a larger health issue?
In some cases, constant eating dreams can be a sign of a larger health issue. If you consistently have dreams where you are constantly eating and are also experiencing other symptoms such as unexplained weight gain or loss, changes in appetite, or digestive problems, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional. These dreams could potentially be a manifestation of an underlying physical or psychological condition that needs to be addressed.
Are there any ways to prevent or reduce constant eating dreams?
While it is not always possible to prevent or reduce constant eating dreams, there are some strategies that may help. One approach is to evaluate your eating habits and ensure you are consuming a balanced diet that satisfies your nutritional needs. Additionally, managing stress and finding healthy ways to cope with emotions can also help reduce the frequency of these dreams. Engaging in relaxation techniques before bed, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, may also promote more peaceful sleep and reduce the occurrence of constant eating dreams.



