Nowadays, many individuals might find themselves facing an unexpected challenge: a fungal infection in their mouth. This perplexing condition, which manifests as tiny white patches or sores, can cause discomfort and even lead to more severe complications if left untreated. Unraveling the underlying causes and discovering suitable treatments is of utmost importance for those affected by this condition.
Unveiling the Culprits: When it comes to the origins of oral fungal infections, various factors can play a role. One common offender is a fungus called Candida albicans, which naturally resides in our mouths. However, when its growth becomes overabundant, it can result in an infection known as oral thrush. Other culprits like certain medications, compromised immune systems, poor oral hygiene, and even certain medical conditions such as diabetes can create an environment ripe for fungal infections to develop.
Confronting the Symptoms: Recognizing the symptoms of oral fungal infections is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Individuals might experience discomfort or soreness in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, the presence of white patches or sores on the tongue, inner cheeks, or throat, and unpleasant taste sensations. It is important to note that these symptoms can vary from person to person and might coincide with other oral conditions, warranting a professional assessment from a healthcare provider.
Seeking Effective Treatments: Thankfully, there are various treatments available to combat oral fungal infections and alleviate the associated discomfort. Antifungal medications, such as oral rinses or lozenges containing agents like fluconazole or nystatin, are commonly prescribed by healthcare professionals. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, using antifungal mouthwashes, and avoiding irritants like tobacco and alcohol, can also aid in the management and prevention of these pesky infections.
In conclusion, understanding the origins and treatments for oral fungal infections is key to successfully managing and overcoming this troublesome condition. By employing an interdisciplinary approach that combines proper oral hygiene practices with the appropriate medications, individuals can regain their oral health and overall well-being. Regular dental check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for timely intervention and the prevention of further complications.
The Basics of Oral Fungal Infections

Exploring the Fundamentals of Fungal Infections in the Oral Cavity
Fungal infections in the mouth are a common oral health problem that can result from various factors. These types of infections, also known as oral candidiasis or oral thrush, occur when a type of fungus called Candida overgrows in the mouth. Understanding the basics of oral fungal infections is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Overview Fungal infections in the mouth affect a significant number of individuals, ranging from infants to elderly adults. They are caused by the overgrowth of Candida, a yeast-like fungus that naturally exists in the oral cavity. Under normal circumstances, the body's immune system keeps Candida in check. However, certain factors can disrupt the balance, leading to the development of oral fungal infections. | Common Symptoms When an oral fungal infection occurs, it can manifest in various symptoms. These may include white patches or plaques on the tongue, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth, or throat. The affected areas may be painful, sensitive, or bleed when disturbed. Other common symptoms include difficulty in swallowing, altered taste perception, and dry mouth. |
Potential Causes Oral fungal infections can arise due to several factors, such as a weakened immune system, certain medications, poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, or underlying medical conditions. Individuals who wear dentures, smoke, or have diabetes are also at a higher risk of developing oral fungal infections. | Diagnosis and Treatment Diagnosing an oral fungal infection often involves a comprehensive examination of the oral cavity and may include taking samples for laboratory analysis. Treatment options typically include antifungal medications, both topical and oral, aimed at killing the fungus and restoring the balance of the oral flora. Practicing good oral hygiene and addressing underlying health conditions are also essential for successful management. |
Prevention Preventing oral fungal infections involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, along with proper denture care. Avoiding excessive sugar consumption, quitting smoking, and managing underlying medical conditions effectively can also reduce the risk of fungal overgrowth. | Conclusion Oral fungal infections are a common oral health issue caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus in the mouth. Understanding the basics of these infections, including their causes and symptoms, is crucial in order to facilitate timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By practicing preventive measures and maintaining good oral hygiene, individuals can effectively reduce their chances of developing oral fungal infections. |
Common Types of Fungal Infections in the Oral Cavity
The oral cavity is susceptible to various types of fungal infections, which can cause discomfort and affect oral health. This section highlights some of the most commonly encountered fungal infections in the mouth, providing an overview of their symptoms and potential treatments.
Oral Thrush: Also known as oral candidiasis, this fungal infection is caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus in the mouth. It often presents as white, cottage cheese-like patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and roof of the mouth. Common symptoms include soreness, redness, and difficulty swallowing.
Angular Cheilitis: This fungal infection mainly affects the corners of the mouth, causing inflammation, cracking, and soreness. It is often caused by an overgrowth of Candida or a combination of Candida and bacteria. Factors such as drooling, ill-fitting dentures, and nutritional deficiencies can contribute to its development.
Oral Histoplasmosis: This infection is caused by inhaling spores of the Histoplasma fungus, which typically grows in soil contaminated with bird or bat droppings. It can affect the mouth, throat, and other organs. Symptoms may include mouth ulcers, difficulty swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes.
Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis: This persistent form of oral candidiasis is characterized by the presence of white lesions that cannot be wiped off. It often affects the borders of the tongue and can be associated with smoking, poorly fitting dentures, or certain medical conditions.
Oral Fungal Biofilms: Biofilms are complex communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces and can cause resistant infections. In the mouth, fungal biofilms can form on dentures, oral tissues, or other surfaces, leading to chronic infections that are difficult to treat.
Seeking prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment options from a healthcare professional is crucial for managing these fungal infections effectively. Treatment may involve antifungal medications, improving oral hygiene, and addressing underlying factors that contribute to the infection.
Risk Factors Contributing to Oral Fungal Infections
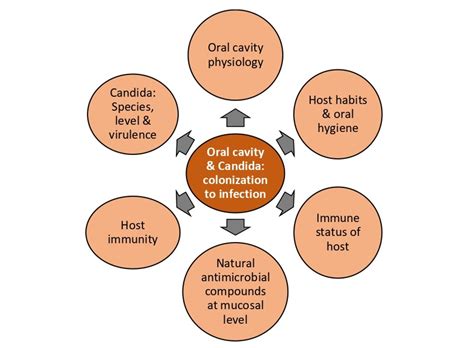
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing fungal infections in the mouth can vary greatly and are influenced by a combination of different elements. These risk factors play a significant role in the susceptibility of individuals to oral fungus, and understanding them can help in identifying those who are at a higher risk.
One of the key factors is compromised immune function, which can be caused by various underlying conditions such as immunodeficiency disorders, certain medications, or undergoing treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Additionally, individuals with diabetes or other chronic illnesses that weaken the immune system may also have an increased susceptibility to oral fungal infections.
Poor oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing or flossing, can create an environment that allows fungi to thrive in the mouth. The presence of factors like dry mouth, which may be caused by medications or specific medical conditions, can further contribute to the growth of fungi. Furthermore, the use of dentures, especially if not properly cleaned and fitted, can create an ideal breeding ground for fungal infections in the oral cavity.
Other risk factors include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain lifestyle choices. These behaviors can weaken the immune system and disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the mouth, making it easier for fungal infections to occur.
| Common Risk Factors for Oral Fungal Infections |
|---|
| Compromised immune function |
| Diabetes or other chronic illnesses |
| Poor oral hygiene practices |
| Denture use |
| Smoking |
| Excessive alcohol consumption |
| Unhealthy lifestyle choices |
Preventive Measures to Minimize the Risk of Oral Fungal Infections
Promoting Healthy Oral Environment: Maintaining a balanced oral microbiome can play a crucial role in preventing the development of fungal infections in the mouth. Creating an environment that is inhospitable for fungal growth can greatly reduce the risk of oral fungal infections.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Consistent and proper oral hygiene practices are essential in preventing oral fungal infections. Brushing your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help eliminate the fungal organisms present in the mouth.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to the dentist are essential for early detection and prevention of oral fungal infections. Dentists can identify any potential risk factors or signs of fungal infections, provide appropriate treatment options, and educate patients on preventive measures.
Dietary Considerations: Including certain foods in your diet can help strengthen your immune system and minimize the risk of oral fungal infections. Consuming foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt and fermented vegetables, can promote a healthy balance of oral flora and inhibit fungal overgrowth.
Avoiding Risk Factors: Identifying and avoiding potential risk factors can be crucial in reducing the risk of oral fungal infections. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, wearing dentures that don't fit properly, and having certain underlying medical conditions like diabetes can increase the vulnerability to fungal infections in the mouth.
Promoting Immune Health: Maintaining a strong immune system is vital in preventing oral fungal infections. Adequate sleep, regular exercise, managing stress, and consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help support immune function and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Proper Oral Care for Denture Wearers: Denture wearers are more prone to oral fungal infections. To minimize the risk, it is important to clean and soak dentures regularly, keep the mouth and dentures clean, and ensure a proper fit and maintenance of dentures.
Education and Awareness: Increasing awareness regarding oral fungal infections and their preventive measures can empower individuals to take proactive steps in minimizing their risk. Proper education on maintaining good oral hygiene, understanding potential risk factors, and seeking timely dental care can contribute to the prevention of oral fungal infections.
Antifungal Medications: In certain cases where individuals are at a higher risk or have a history of recurrent oral fungal infections, antifungal medications may be prescribed as a preventive measure. These medications work to inhibit fungal growth and reduce the likelihood of infection.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of oral fungal infections, promote oral health, and maintain a healthy oral environment.
Diagnostics and Detection of Oral Fungal Infections

Exploring the diagnostic methods and detection techniques for identifying oral fungal infections can aid in early intervention and effective treatment. This section focuses on the various approaches employed to accurately diagnose and detect fungal infections in the mouth.
Treatment Options for Oral Fungal Infections
In this section, we will explore various approaches and methods for addressing fungal infections in the mouth. We will discuss the available treatments and options that can effectively combat these infections, presenting a range of strategies to restore oral health and eliminate fungal concerns.
- Antifungal Medications: One of the primary treatment options for oral fungal infections is the use of antifungal medications. These medications work by targeting and eliminating the fungus responsible for the infection. Depending on the severity of the infection, antifungal medications may be prescribed in the form of oral tablets, lozenges, or topical creams.
- Oral Rinses: Another approach for treating oral fungal infections is through the use of antifungal oral rinses. These rinses contain specific ingredients that help to kill the fungus and reduce the infection. They are often used as a complementary treatment alongside other medications or as a preventive measure.
- Probiotics: Probiotics, such as certain strains of bacteria or yeasts, have shown potential in treating oral fungal infections. These beneficial microorganisms can help restore the natural balance of microflora in the mouth, inhibiting the growth of harmful fungi. Probiotics can be consumed in various forms, including capsules, yogurts, or oral sprays.
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential in preventing and treating fungal infections in the mouth. Proper brushing and flossing techniques, along with regular dental cleanings, can help remove plaque and reduce the risk of fungal overgrowth. Using antifungal mouthwashes or rinses regularly can also aid in controlling fungal activity.
- Dietary Changes: Some dietary adjustments may be beneficial in managing oral fungal infections. Avoiding foods high in sugar and yeast can help starve the fungus and prevent further growth. Including probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt or fermented vegetables, in the diet may also promote a healthy oral environment.
- Home Remedies: Certain home remedies may provide relief and support in addressing oral fungal infections. These may include rinsing the mouth with saltwater, using natural antifungal agents like tea tree oil or coconut oil, and consuming garlic or raw honey, known for their potential antimicrobial properties.
It is important to note that the most appropriate treatment option may vary depending on the specific type and severity of the fungal infection. Consulting with a healthcare professional or dentist is crucial in determining the best course of action for effectively treating oral fungal infections.
Effective Home Remedies for Treating Oral Fungal Infections

Exploring holistic approaches to combating oral fungal infections can provide valuable insights into alleviating this common condition. By incorporating homemade treatments using natural ingredients, you can effectively address the symptoms associated with oral fungus while promoting overall oral health. Discovering effective home remedies offers individuals an accessible and affordable option for managing oral fungal infections.
FAQ
What are the potential causes of fungus in the mouth?
Fungus in the mouth, also known as oral thrush, is usually caused by an overgrowth of a specific fungus called Candida albicans. It can occur due to various factors such as weakened immune system, poor oral hygiene, certain medications, hormonal changes, and underlying medical conditions.
How is fungus in the mouth diagnosed?
To diagnose fungus in the mouth, a healthcare professional will typically perform a visual examination of the mouth and may also take a sample of the affected area for further analysis. The sample may be examined under a microscope or sent to a laboratory for culture testing to identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
What are the common symptoms of fungus in the mouth?
Common symptoms of fungus in the mouth include white or creamy lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, or other areas of the mouth, redness and soreness, difficulty swallowing or eating, a cotton-like feeling in the mouth, loss of taste, and mouth dryness.
What are the available treatments for fungus in the mouth?
Treatment for fungus in the mouth usually involves antifungal medications, such as oral rinses or lozenges, which are used to kill the fungus. In some cases, systemic antifungal medications may be prescribed. It is also important to practice good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, and to address any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to the growth of oral fungus.
Can fungus in the mouth be prevented?
While it may not always be possible to prevent fungus in the mouth, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. These include maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding excessive sugar consumption, quitting smoking, managing stress levels, and seeking prompt treatment for underlying medical conditions that may weaken the immune system.



